Tags
Abrupt Climate Change, AMOC, Antarctic Ice Melt, Anthropocene Mass Extinction, Arctic Ice Melt, Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, Blue Acceleration, Canfield Ocean, Capitalism, Carbon Dioxide, Climate Change, CO2, Cretaceous–Paleogene Extinction Event, Dr. Peter Ward, Fossil Fuel Dependency, Gerald Durrell, Great Acceleration, Gulf Stream, Hothouse Earth, Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S), IPCC, Jet Stream, K-T Extinction, Loss of Biodiversity, Megadrought, Methane, Micro-Plastic Pollution, Nate Hagens, Nicholas P. Money, Ocean Acidification, PETM Extinction Event, Sea Level Rise, Social Media Algorithms, Widespread Ocean Anoxia
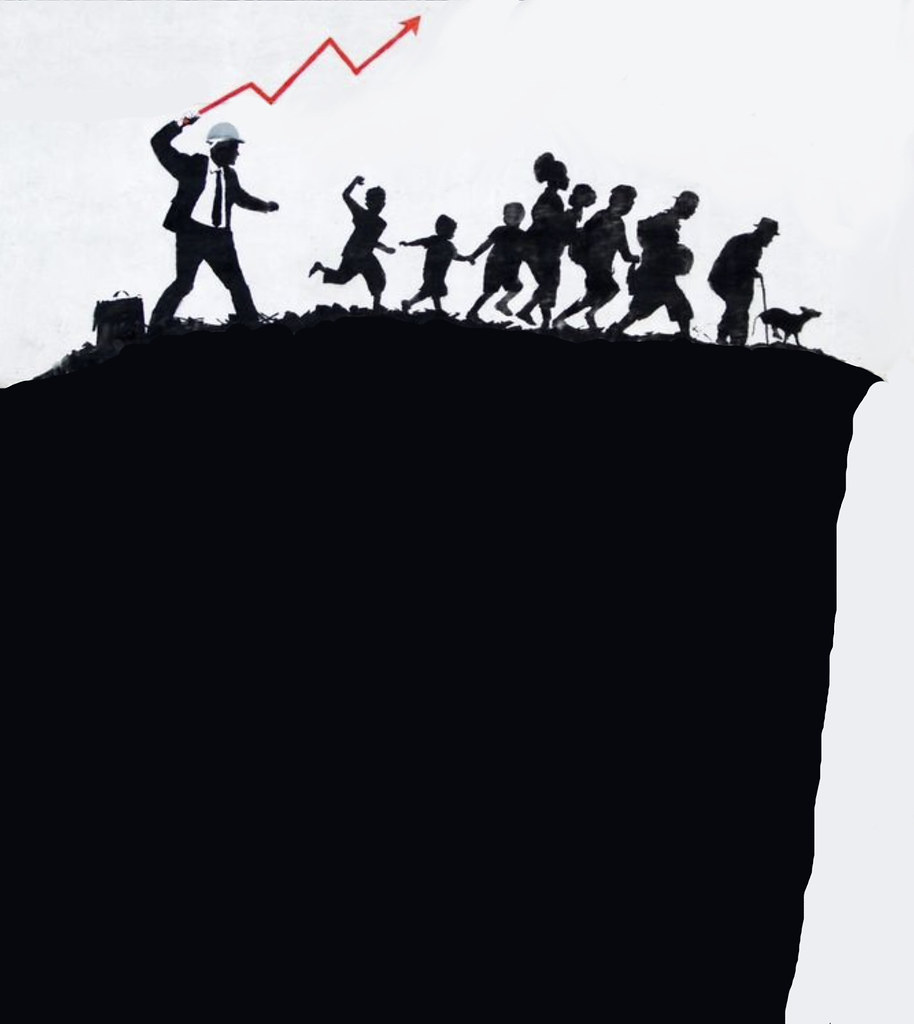

Nate Hagens’ recent interview of Professor Peter Ward, entitled “Oceans – What’s the Worst that Can Happen?”, serves as a good overview of mankind’s destruction of the marine biosphere and our road to extinction. The title is a rather rhetorical question because very bad things have happened, are already happening, and even worse things are unavoidable and on the horizon despite hopes that humans will run out of ways to extract the dirtiest and most inaccessible fossil fuel deposits. We have seen how inextricably linked economic growth is to rising fossil fuel consumption, no matter the mounting disasters happening before our eyes and the steady stream of dire warnings issued from the scientific community. The most current of such warnings came from the UN last month, and it states that escalating synergies between disasters, economic vulnerabilities and ecosystem failures are increasing the risk of a “global collapse” scenario. Such a catastrophic scenario appears all but inevitable. Constricting fossil fuel consumption is like squeezing a balloon. If one country stops consumption, another takes up the slack. For example, efforts to cripple Russia’s fossil fuel exports for their unwarranted invasion of Ukraine don’t appear to be very effective since China and India have simply stepped in and increased their purchases. Rising oil prices have also more than offset a decline in Russia’s export volumes. Perhaps an unintended consequence of those higher energy prices will be the ripple effect through the economy, making food unaffordable for large swaths of the globe and destabilizing governments.
Getting back to the Peter Ward interview, the professor states matter of factly, “Every time we get into a car, it’s putting more of those CO2 particles into the atmosphere. And if this isn’t collective suicide by Homo sapiens, I don’t know what is.” Unfortunately for us, humans have created an unsustainable civilization supporting billions of people while at the same time destroying the very foundation upon which that system is dependent. Humans are by far outperforming the carbon-spewing volcanoes of past mass extinctions. Nicholas Money, renowned mycologist and author of many books, recently wrote:
Decades ago, Gerald Durrell, the famous conservationist, recognized that “the human race is in the position of a man sawing off the tree branch he is sitting on.” Thirty years after Durrell’s death, the human population has increased by 2 billion and the damage has intensified. The branch will snap now whether we keep sawing or not.
The timeline for extinctions is not known, but, sooner or later, the disappearing mammals will be joined by the other groups of animals. Almost everything will be leaving the metaphorical ark, creeping down the gangplank into oblivion. Millions of other species, seen and unseen, including plants, seaweeds, and fungi will be leaving, too. The tiniest of organisms will inherit the planet, but great gulps of the microbial world will also disappear in the depths of this planetary holocaust…
Exact dates are not known, but mankind’s final fate can be seen scrawled upon the familiar checklist for mass extinctions which we are quickly ticking off, one by one. As Ward points out, every time there has been a major disruption in Earth’s delicate biogeochemical carbon cycle, there has been a mass extinction. Today that disruption is happening on a timescale much faster than at any time in the past, even faster than the asteroid impact that killed off the dinosaurs. During the K-T extinction, the immediate impact of the asteroid killed only the large animals. It took thousands of years for the consequent climate change to kill off smaller organisms. Current trends are exponentially faster, not only with anthropogenic climate disruption incinerating the biosphere within a lifetime but also by a multi-pronged attack from other human activities such as chemical and plastic pollution, the global spread of invasive species, and humanity’s massive overdraw on the planet’s resources.

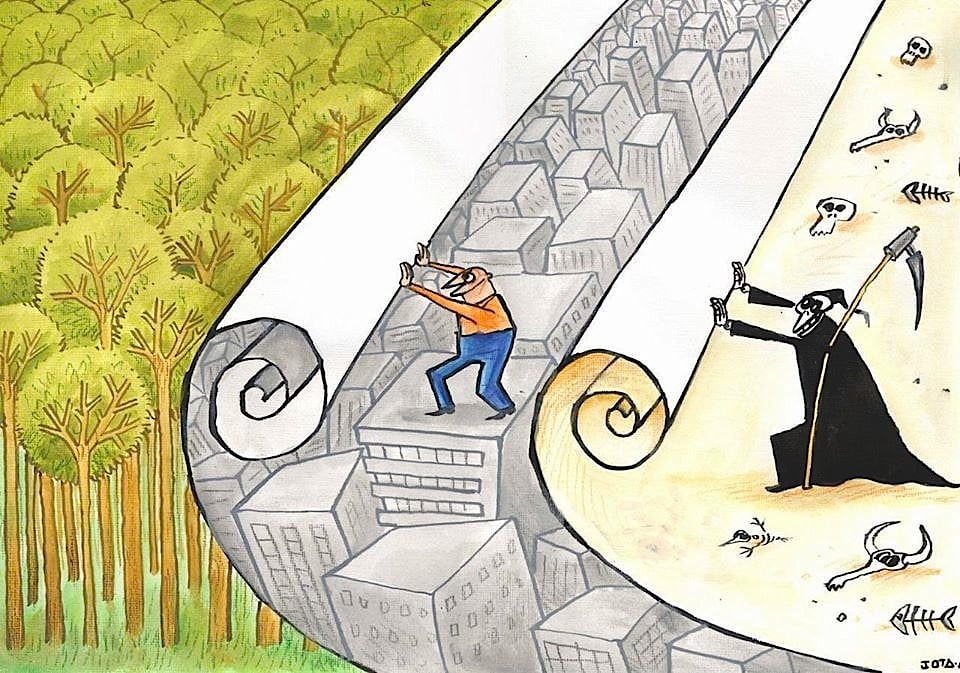
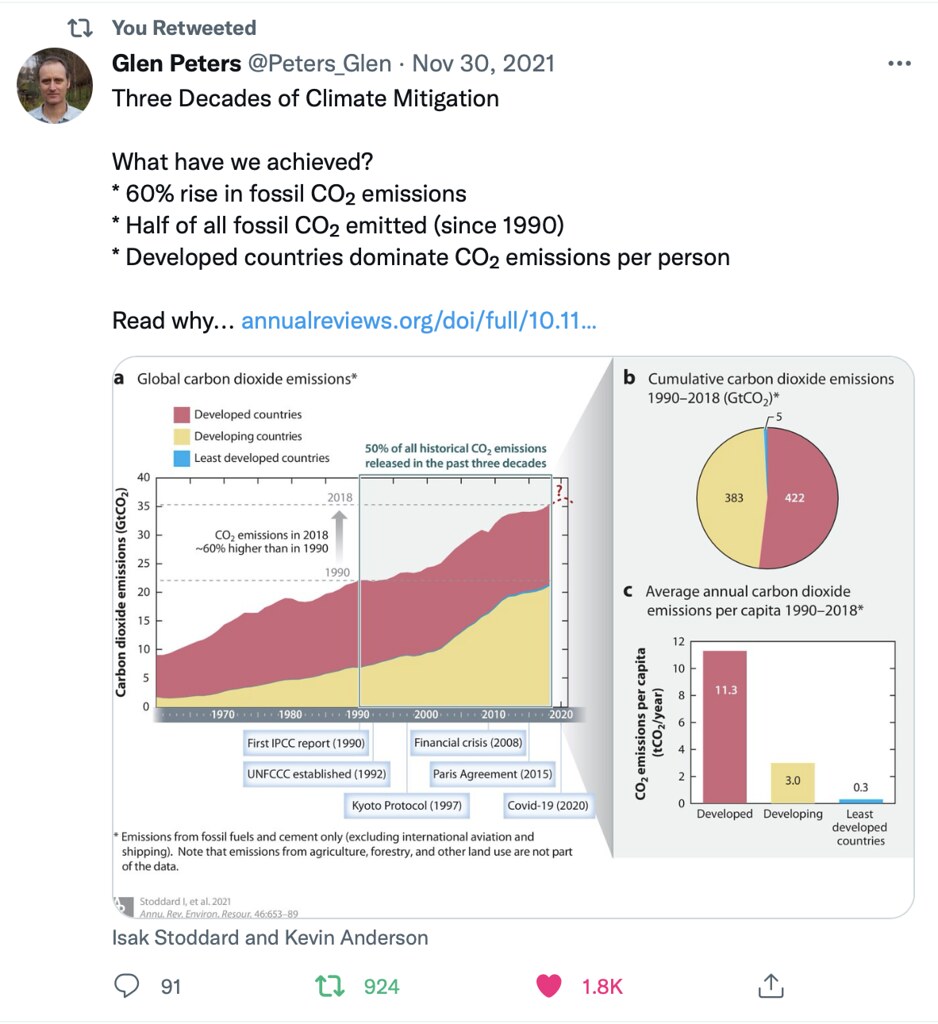
If one were to equate Earth’s geologic history to a calendar year, modern humans have been around for a mere 37 minutes while managing to consume 1/3rd of Earth’s natural resources in just the last 0.2 seconds. The biomass of wild mammals has fallen by 83% since prehistory and it is projected that by 2050 humans will have eliminated 38–46% of all biodiversity from the planet. 70% of the planet’s land area has been altered by humans, with 40% considered degraded. By 2050, an area of land the size of South America will be further degraded. Nearly all of the marine biosphere has been degraded. Now Modern man has set his sights on wringing the last dollar of profit from the already dying oceans in what is being heralded as the “Blue Acceleration”, a not-so-clever play of words on the Great Acceleration referring to the period starting around 1950 when measurements of humanity’s impact on the planet’s resources went hyperbolic:
As pressures on Earth’s land grow and terrestrial resources look increasingly exhausted, governments and corporations are seeing the next big wins on, in and under the high seas. Whether it is mineral exploration, shipping, energy, tourism, desalination, cable laying, bioprospecting or more, ocean-based industries are picking up speed fast.
This “blue acceleration” has many people worried…With the power to profit from remote ocean resources growing rapidly, and the laws that govern their exploitation less than clear, we risk a free-for-all in the deep. “Our society has been based on the degradation of nature, destruction of nature,” says marine ecologist Enric Sala…
The new plunge into the ocean has come about in part because technologies – from ocean drilling and offshore wind turbines to desalination plants and factory trawlers – have made it possible. “A lot of offshore industries were unthinkable even just a few decades ago,” says Jouffray.
And so it goes, Homo sapiens onward march of eating the seed corn and leaving a husk of a planet for future generations …if there are to be any.
Back to Peter Ward and that checklist for mass extinction…The second step after a large release of heat trapping gasses is that Earth’s poles will start warming up much faster than the rest of the globe, melting the polar icecaps and reducing the heat differential between the equator and higher latitudes. A recent study found that the Arctic is heating up as much as seven times faster than the global average. The Antarctic is warming four times faster than the global average. This diminishing heat differential between the higher latitudes and the equator leads to the third step which is that ocean currents and atmospheric jet streams slow down and become stagnant and swampish. As professor Ward points out, swamps have a lot of nasty, toxic aspects to them such as hydrogen sulfide. This has happened to the oceans many times in Earth’s history with deadly consequences, the most recent being the PETM extinction which was associated with the largest deep-sea mass extinction event in the last 93 million years. Less than 5% of sea creatures survived. The oceans became a poisonous and miasmic brew of acidification, hypoxia and sulfide gases. Deep ocean upwellings injected hydrogen sulfide into the atmosphere, laying waste to plants and animals. This killer gas rose to the upper atmosphere and also attacked the ozone layer, allowing deadly ultraviolet radiation from the sun to amplify the destruction of plant and animal life. Fossil spores contained in strata from the PETM extinction show deformities consistent with damage from UV radiation. Major disruptions in the hydrologic cycle occurred with evidence of increased continental runoff. Land suffered extreme precipitation events. Dinoflagellates, tiny organisms that ooze toxins and create deadly algal blooms called ‘red tides’, flourished in the nearly 100°F surface water of the equator. Less than a third of the large animal species made it. Nearly all trees died. No ice existed on the planet during that time. Sea levels were around 300 feet higher than now.
Today we are pumping heat trapping gases into the atmosphere nine to tens times higher than during the PETM extinction. We are just four generations away from matching the chemical composition of the atmosphere that caused that die-off event. However, we are already seeing major changes in the Earth’s climate system that align with the third step toward a mass extinction. Proxy data (like coral data, ocean sediments, and land-based data) along with modern-day instrumentation show an intense weakening of the AMOC, Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, in the past 200 years. And the Gulf Steam, a component of the AMOC, is also showing signs of collapse. We are in the process of turning off the global ocean conveyor belt that keeps the ocean oxygenated and helps regulate the Earth’s climate. Ocean acidity has increased about 30% from preindustrial times to the early 21st century, a pace faster than any known in Earth’s geologic past. The volume of anoxic ocean waters has quadrupled since the 1960s, and evidence suggests that temperature increases explain about 50% of oxygen loss in the upper 1000 meters of the ocean. Ocean stratification due to climate change has increased 18% in the top 150 meters of the oceans since 1960. Stratified ocean layers have a number of negative effects such as preventing the mixing and transport of heat, carbon dioxide, oxygen, and nutrients to the lower depths of the oceans. It was only recently, November 2021, that a group of scientists issued a plea to governments for establishing a global monitoring system to track the loss of oxygen in the oceans causing dead zones:
“There is a pressing need to document and predict hypoxic episodes and hotspots of low oxygen in order to take protective actions for aquaculture, put in place precautionary measures for affected fisheries, and monitor the wellbeing of important fish stocks,” Limburg said.
“Without this understanding, we are in the dark about impacts that have large economic-ecological implications.”…
“These problems are getting worse because we are not solving the problems of nutrient run-off and our waters are continuing to warm.
Stalled Rossby waves in the Jet Stream linked to extreme weather events have increased significantly in the last twenty years. U.S. crop losses due to drought and flooding have trippled since 1995. Onward we march into oblivion.
Despite the horrors described thus far, what really scares Professor Ward is sea level rise. Ward believes that the volcano of mankind will sputter out before we reach the levels required for a full-fledged Canfield Ocean, and negative feedback loops in the climate system will pull Earth back from the brink. The “Canfield Ocean”, a sulfidic and partially oxic ocean, existed for more than 40% of Earth history, between the Archean and Ediacaran periods. It would take millennia to reach that state again, but humans are supercharging the process to get there by releasing into the ocean vast quantities of nutrients from agricultural fertilizer, soil erosion, industrial waste and sewage, in addition to the ever-growing release of CO2 and methane emissions. Humans have become a geologic force breaching most if not all of the planetary boundaries that make Earth hospitable for life. The mechanisms required for Earth to return to a dead, toxic planet may have already been irreversibly set into motion.
Getting back to Ward’s fear, the most recent report on sea level rise states that it is accelerating with an increase of one foot expected along U.S. coasts by 2050. And that is only if emissions are curbed now. Otherwise, expect up to 5 feet. The researchers say that one foot of SLR over the next three decades is equal to the total that occurred over the past century. Just one foot of vertical rise in sea level will swallow up 100 feet of shoreline if the slope is just 1% or more, a typical slope for most coastlines. To make matters worse, most coastal cities are sinking at a rate faster than the seas are rising. Thus within the next few decades, we could see several hundred feet of shoreline swallowed up along coasts of America and around the world, creating the largest human migration in history. Ward believes we’ll have six feet of sea level rise by 2080 which will destroy a big percentage of the world’s rice production, primarily through salinization. Rice is the number one food source for a majority of the world population today. Sea level rise alone could devastate global trade, not to mention the inevitable damage to ports from stronger storms. The latest IPCC report made it clear that parts of the planet are fast becoming uninhabitable:
Life in some locations on the planet is rapidly reaching the point where it will be too hot for the species that live there to survive, international climate experts said in a report Monday.
“With climate change, some parts of the planet will become uninhabitable,” said German scientist Hans-Otto Pörtner, co-chair of Working Group II for the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), which produced the report released in Berlin…
…Increased heat waves, droughts and floods are already exceeding plants’ and animals’ tolerance thresholds, driving mass mortalities in species such as trees and corals, according to the report…
…Sherilee Harper, a lead author on the North American chapter and an associate professor at the University of Alberta’s public health school, said she was personally struck by the effect climate change already is having on the “physical and mental health of many Americans.”
Peter Ward then brings up something I don’t remember hearing about global warming. The higher temperatures are disrupting the sperm fertility of organisms. Ward says it’s an existential threat to the amount of food we can produce. Recent studies show this to be true and the damage continues across generations:
…according to new research. New findings reveal that heatwaves damage sperm in insects – with negative impacts for fertility across generations. The research team say that male infertility during heatwaves could help to explain why climate change is having such an impact on species populations, including climate-related extinctions in recent years.

Nate and Peter then get into the societal ignorance preventing humans from addressing any serious problem, let alone the existential threat of anthropogenic climate disruption. Peter says, “How could we, as a species, take something as simple as masks and turn it into a political ploy where the level of ignorance will kill you, will kill you?!?” Nate then explains how social media algorithms are set up to highlight the most polarizing content in order to generate more user activity since their business model is based on user engagement. In order to keep users online, the social media platforms are also designed to be very addictive such as with the infinite scroll feature and the “like” button.
In 2017, Facebook’s former president, Sean Parker, said publicly that the company sought to consume users’ time as much as possible, and that the act was “exploiting a vulnerability in human psychology”…”That means that we needed to sort of give you a little dopamine hit every once in a while because someone liked or commented on a photo or a post or whatever… It’s a social validation feedback loop… You’re exploiting a vulnerability in human psychology…” – link
There is no fixing this dysfunctional social media ecosystem because it is operating exactly as intended. Our profit-driven economic system is rooted in inequality, exploitation, dispossession, and environmental destruction. And encouraging the public to turn off the horror show of climate chaos and biodiversity annihilation are essential for this system to continue. Exploiting tribal biases is a good way to keep the plebs fighting amongst themselves as the last dollar is extracted from a dying planet. Nate asks, “If we can’t have a discussion on what’s real or not with COVID, how are we going to have one about the ocean’s ecosystems and Earth systems and our collective future?” Indeed.